In today’s visually-driven digital landscape, images are more than just aesthetic additions; they are powerful **SEO assets** waiting to be optimized. While text content often takes center stage in SEO discussions, the optimization of images and their corresponding links is crucial for a **holistic search engine strategy**. This guide will delve into the intricacies of **SEO for image links**, helping you understand how to leverage them to drive traffic, improve user experience, and ultimately, enhance your overall search engine rankings.

Why Image Link Optimization Matters for SEO
Many website owners overlook the **SEO potential** of their images. However, search engines like Google don’t just crawl text; they also analyze image data to understand content relevance. **Optimizing your image links** contributes to:
- **Improved Search Engine Rankings:** Properly optimized images can appear in Google Images, driving additional traffic to your site.
- **Enhanced User Experience:** Fast-loading, relevant images keep users engaged and reduce bounce rates.
- **Increased Discoverability:** Descriptive alt text and filenames make it easier for search engines to understand and categorize your images, leading to better visibility.
- **Accessibility:** Alt text is vital for visually impaired users who rely on screen readers.

Key Strategies for SEO Optimization of Image Links
1. Descriptive Filenames are Your First Step
Before you even upload an image, ensure its filename is descriptive and **keyword-rich**. Instead of “IMG_001.jpg,” use something like “seo-optimization-guide.jpg” or “google-search-console-dashboard.webp.” This provides search engines with immediate context about the image’s content.

2. Craft Compelling Alt Text
**Alt text** (alternative text) is perhaps the most critical element for **image SEO**. It describes the image to search engines and visually impaired users. Be descriptive, include your **focus keyword** naturally, and avoid keyword stuffing. For example, for an image of a Google Search Console dashboard, good alt text would be: “Screenshot of **Google Search Console** dashboard showing performance data.”


3. Image Compression and Page Speed
Large image files can significantly slow down your website, negatively impacting user experience and SEO. **Compress your images** without sacrificing quality. Tools and plugins can help with this. Google’s **PageSpeed Insights** is a valuable resource for identifying and fixing page speed issues.

For more insights into optimizing your site for speed, consider resources like Neil Patel’s blog or the Ahrefs blog.
4. Choose the Right Image Format
WebP, JPEG, and PNG are common image formats. **WebP** often offers superior compression while maintaining quality, making it an excellent choice for web images. JPEG is good for photographs, and PNG is ideal for images with transparency or sharp lines.


5. Image Sitemaps
An **image sitemap** helps search engines discover all the images on your site, especially those that might not be found through regular crawling. You can submit image sitemaps through Google Webmaster Tools.

6. Contextual Relevance and Surrounding Text
Place images within relevant text content. The text surrounding your image helps search engines understand its context and relevance to your overall content. For instance, if you’re discussing where to buy Quran, an image of a beautifully bound Quran should be accompanied by text discussing its purchase options.
Consider our cornerstone article: **Quran Shop Near Me: Your Guide to Finding Quality Qurans Locally**. Images within this article, such as different editions of the Quran or local shop fronts, would be highly relevant.

7. Responsive Images
Ensure your images are **responsive**, meaning they adapt to different screen sizes (desktops, tablets, mobile phones). This is crucial for **mobile SEO** and user experience. Tools and CSS can help implement responsive image practices.


8. Internal Linking to Image Pages (if applicable)
If your images have their own dedicated pages (e.g., in a gallery or portfolio), ensure they are **internally linked** from relevant content. This helps distribute link equity and improves crawlability. For instance, if you have a page on Quran purchase, you might link to an image gallery showcasing different Quran covers.

9. Monitor Image Performance
Regularly check your image performance in **Google Search Console**. Look for any crawling errors or issues that might prevent your images from being indexed. Utilize tools like Moz’s SEO tools or Search Engine Journal for broader SEO insights.

—
LSI Keywords to Enhance Image Link SEO
Beyond your main focus keyword, incorporate **Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords**. These are semantically related terms that help search engines better understand the context of your content and images. For an article on “**SEO optimization**,” LSI keywords could include:
- Search engine rankings
- Website traffic
- Keyword research
- On-page SEO
- Technical SEO
- Content marketing
- Backlinks
- User experience
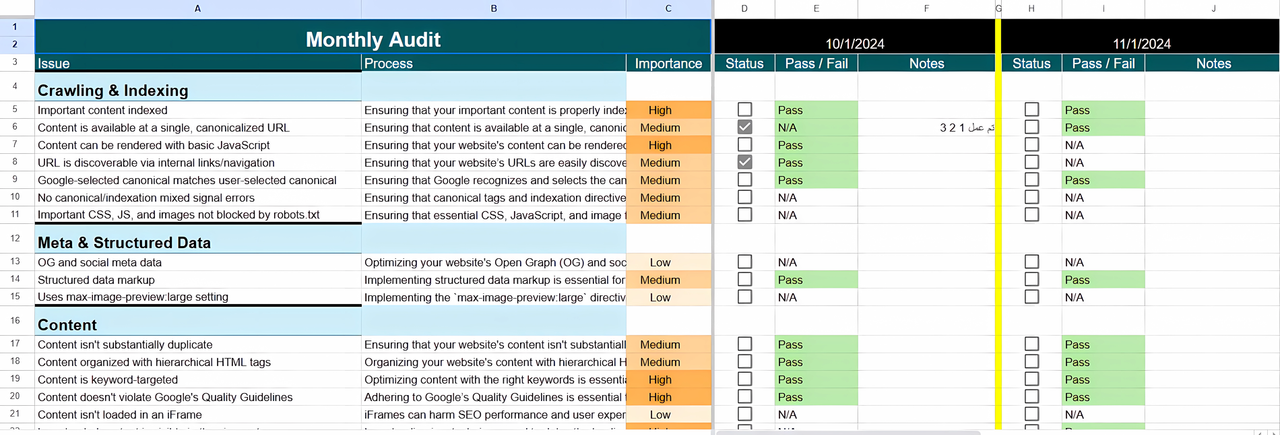
Think about how these **LSI keywords** can naturally be integrated into your image filenames, alt text, and the surrounding content. For example, an image demonstrating local business listings could have alt text like: “Local business listing showing enhanced visibility from **local SEO** strategies.”

—
Leveraging Image Links for Specific Content Types
E-commerce Product Images
For e-commerce sites, product images are paramount. Optimize them with specific product names, model numbers, and descriptive features in alt text. This aids in product discovery through image search.
If you’re looking to buy Quran or order Quran online, high-quality, optimized images of the different editions are essential for customer engagement and SEO.
Informational Graphics and Infographics
If you create infographics or data visualizations, optimize them thoroughly. These can be powerful link-building assets. Ensure the alt text summarizes the infographic’s key takeaway. For example, an infographic on SEO trends:


Blog Post Images
Every image in your blog posts should serve a purpose and be optimized. This includes featured images, in-content images, and even social sharing images. A blog post discussing **Google Ads secrets** would benefit from relevant screenshots with clear alt text.



—
Continuous Learning and Resources
The world of SEO is constantly evolving. Stay updated with the latest best practices through reputable sources:
- Coursera and Udemy offer excellent SEO courses.
- Edraak provides valuable educational content.
- Follow industry leaders and blogs like the Moz SEO Guide and Backlinko Blog.








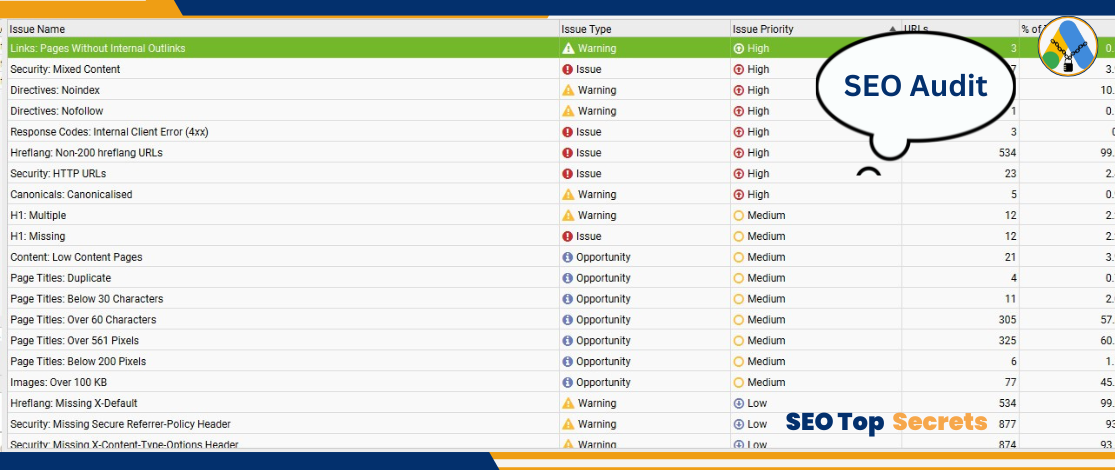








—
Conclusion
**Optimizing your image links for SEO** is no longer an option but a necessity for maximizing your online visibility. By implementing descriptive filenames, compelling alt text, efficient compression, and strategic placement, you can transform your images from mere visuals into powerful **SEO assets**. Remember to consistently monitor your efforts and adapt to the ever-evolving SEO landscape. A comprehensive approach to SEO, including robust **image optimization**, will ensure your content reaches its full potential and stands out in search results.
—
FAQ
Q1: What is the most important factor for image SEO?
A1: Descriptive and keyword-rich **alt text** is arguably the most important factor for image SEO. It provides search engines with context about the image and improves accessibility.
Q2: How does image compression affect SEO?
A2: Image compression directly impacts **page load speed**. Faster loading pages provide a better user experience and are favored by search engines, leading to improved rankings. Therefore, efficient image compression is crucial for SEO.
Q3: Should I include keywords in image filenames?
A3: Yes, absolutely. Including relevant **keywords in your image filenames** (e.g., “blue-running-shoes.jpg” instead of “image1.jpg”) provides another signal to search engines about the image’s content.
Q4: What is an image sitemap and why do I need one?
A4: An **image sitemap** is an XML file that lists all the images on your website, helping search engines discover and index them more efficiently, especially images that might not be found through regular crawling. It’s particularly useful for websites with a large number of images.
Q5: How often should I review my image SEO?
A5: It’s good practice to periodically review your **image SEO**, especially when updating content or adding new images. Regularly checking your Google Search Console for image-related errors and monitoring image performance can help you stay on top of your optimization efforts.
“`